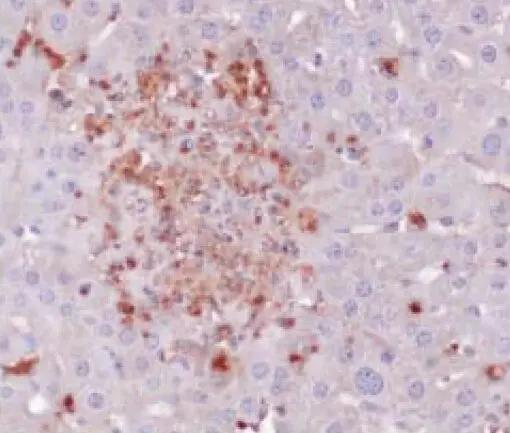
Toxoplasma is a crescent-shaped sporozoan that lives as an intracellular parasite in various tissues of many vertebrates and completes its life cycle in a single host. Its life cycle includes two phases called the intestinal (or enteroepithelial) and extraintestinal phases. The intestinal phase produces oocysts and occurs only in cats, wild as well as domesticated. The extraintestinal phase occurs in all infected animals including cats, and produces tachyzoites (actively proliferating trophozoites) and eventually, bradyzoites (slowly growing trophozoites) or zoitocysts. Infection due to Toxoplasma gondii occurs in pregnant women where a variable degree of immunosuppression may exist or in patients receiving immunosuppressive drug therapy. Toxoplasma infects tissue of the GI tract, where an active infection is accompanied by fever and enlargement of the spleen. Symptoms of toxoplasmosis are generally mild, but severe infection of lymph nodes may occur. Congenital toxoplasmosis, in which the maternal infection is transmitted during pregnancy, can produce blindness or mental retardation in the newborn.
Catalog No. RC0260
Clone
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Host species
Rabbit
Species Reactivity
Whole organisms
Cellular Localization
Whole organisms
Positive Control
infected brain tissue
Applications
ELISA, ICC/IF, IHC
Intended Use
Research Use Only