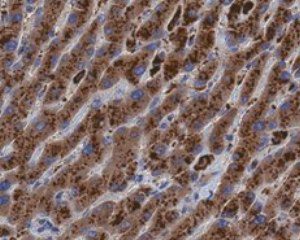
Cathepsin B (CSTB), part of the papain family of proteases, is a widely expressed lysosomal cysteine endopeptidase. Cathepsin B is produced from a larger precursor form, pro-cathepsin B, which runs at approximately 44 kDa on SDS-PAGE, and is proteolytically processed and glycosylated to form a mature two-chain protein containing a heavy chain (running at 27 and 24 kDa) and a light chain (5 kDa). High levels of cathepsin B are found in macrophages and osteoclasts, as well as various types of cancer cells, including lung, colon, prostate, breast, and stomach. In addition, expression of cathepsin B has been associated with multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and pancreatitis. While generally localized to lysosomes, in cancer alterations can lead to its secretion. Its role in tumor progression is thought to involve promotion of basement membrane degradation, invasion and metastasis. Expression can correlate with poor prognosis for a variety of forms of cancer.
Clone
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Host species
Rabbit
Species Reactivity
Human, rat
Cellular Localization
Lysosome, melanosome, can be secreted or associated with plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus
Positive Control
HeLa cells, HT1080, A375, SW480 & A549 cell line lysates; colon carcinoma
Applications
IHC, WB
Intended Use
Research Use Only