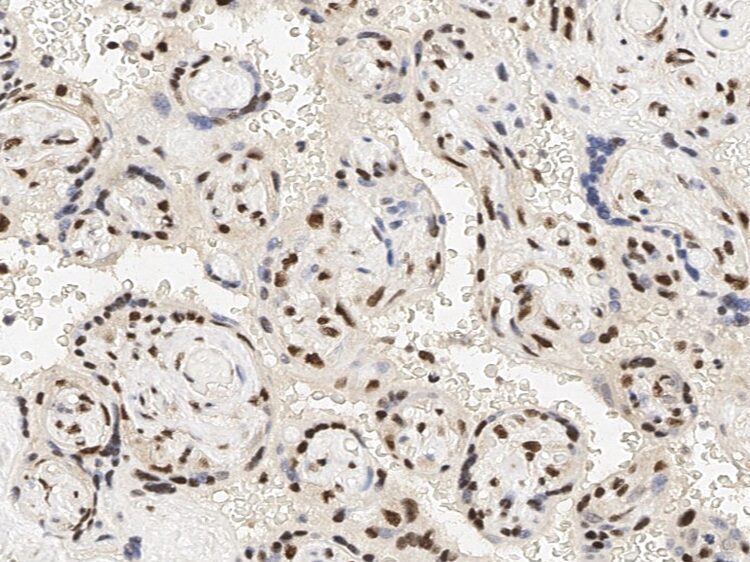
RNA-binding proteins have a pivotal role in post-transcriptionally regulating gene expression. During early development they exhibit temporally and spatially regulated expression pattern, and affect the proteome of a single cell by controlling alternative splicing, transport, localization, and stability of their target RNAs. Their expression is tissue-specific, and their crucial influence on the protein set-up, especially in muscle cells, has become recognized recently. RBM24 is one RNA-binding protein and plays a fundamental role in regulating cardiac gene expression, sarcomeric assembly, and cardiac contractility and may thus represent a novel pathway to cardiomyopathy. RBM24 Plays a role in myogenic differentiation by regulating MYOG levels. Binds to the 3′-UTR of MYOG mRNA and regulates its stability. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing.
Catalog No. RC0296
Clone
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Host species
Rabbit
Species Reactivity
Human, mouse, rat
Cellular Localization
cytoplasm, nucleus
Positive Control
skeletal muscle tissue
Applications
ELISA, IHC
Intended Use
Research Use Only